Abstract
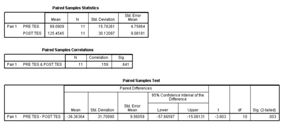
Puskesmas as a health facility has Hazardous and Toxic Materials and the waste that can pollute and / or damage the environment, and / or endanger the environment, health, and survival of humans and other living things. Approximately 70 - 90% of solid waste derived from health installations is a common waste that resembles household waste and does not contain risks. The remaining 10 -25% is waste that can cause various types of health impacts because it is considered dangerous. This community service aims to improve understanding of Hazardous and Toxic Materials management in Ngasem Health Center. This research method uses quantitative approach and data analyzed using Paired sample t-test, significance level α=0.05. The average pretest research results obtained before the socialization of Hazardous and Toxic Materials management is 89.09. After socialization, the average posttest value is 125.45. The significance value of paired t test 0.003 which shows there is a significant influence of socialization on the understanding of B3 management in Ngasem Health Center, Kediri. To reduce the danger / risk due to services performed by puskesmas, the implementation of Hazardous and Toxic Materials management in accordance with standards must be done immediately.
Keywords: Hazardous and Toxic Materials Management, Puskesmas, Socialization

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright (c) 2023 Lembaga Layanan Pendidikan Tinggi Wilayah X